Personal Background
Born on October 11, 1967, in Frankfurt, West Germany.
His family moved frequently due to his father’s career as a chemical engineer. They lived in South Africa and Namibia before settling in the U.S.
Moved to the United States as a child and grew up in Cleveland, Ohio, before settling in California.
Thiel spent part of his childhood in Cleveland but moved to Foster City, California, where he attended high school. His experiences in California shaped his future libertarian views.
Earned a Bachelor’s degree in Philosophy (1989) and a J.D. (1992) from Stanford University.
Thiel initially wanted to become a professor, but he became disillusioned with academia and pursued law instead.
Co-founded The Stanford Review, a conservative-libertarian student newspaper.
Thiel and his peers created the newspaper to challenge what they saw as Stanford’s left-leaning academic environment. The publication remains active today.
Worked as a clerk for Judge James Larry Edmondson and later as a securities lawyer before entering finance.
He spent a short time practicing law at Sullivan & Cromwell in New York but disliked it, leading him to pivot into finance and entrepreneurship.
Entrepreneurial & Business Career
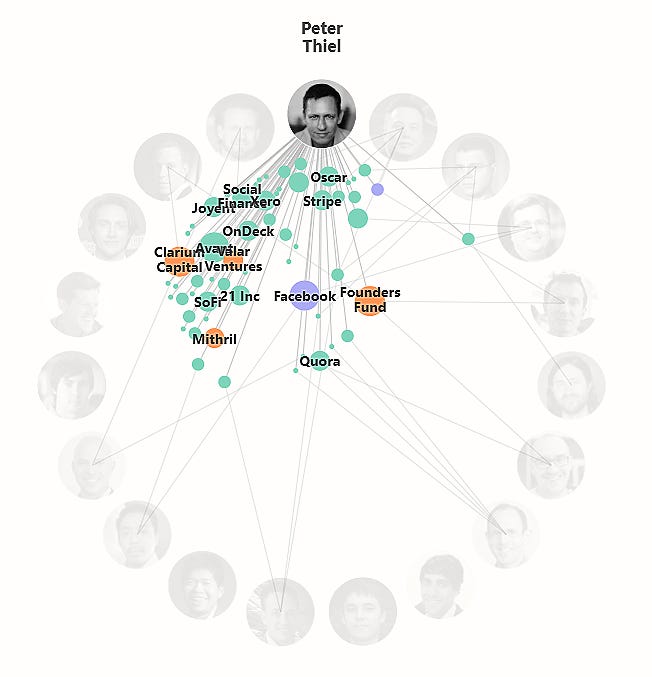
Co-founded PayPal in 1998 with Max Levchin and later merged with X.com, Elon Musk’s online payment company.
PayPal started as a way to facilitate secure online payments. After merging with Musk’s X.com in 2000, Thiel became the CEO and helped refine its fraud detection algorithms.
Served as CEO of PayPal until 2002, when it was sold to eBay for $1.5 billion.
Under his leadership, PayPal grew rapidly, disrupting traditional banking. When eBay acquired PayPal, Thiel earned about $55 million from the sale.
Co-founded Clarium Capital, a hedge fund, in 2002, but it later struggled with performance.
Initially, Clarium performed well, capitalizing on macroeconomic trends. However, it later suffered losses, and its assets under management dwindled.
Was the first outside investor in Facebook, investing $500,000 for a 10.2% stake in 2004.
Thiel met Mark Zuckerberg and saw the potential for Facebook to revolutionize social networking. He later sold most of his shares for over $1 billion.
Co-founded Palantir Technologies in 2003, a data analytics company heavily used by government agencies.
Palantir provides advanced data analysis for intelligence, military, and financial sectors. It has contracts with the CIA, FBI, and other government agencies.
Launched Founders Fund in 2005, a venture capital firm focused on disruptive technology.
Founders Fund invested early in companies like SpaceX, Airbnb, and Stripe. It prioritizes high-risk, high-reward tech ventures.
Invested in Airbnb, LinkedIn, Yelp, and SpaceX through Founders Fund.
His early bets on tech startups helped solidify his reputation as one of Silicon Valley’s top venture capitalists.
Helped launch Mithril Capital, a late-stage investment firm, in 2012.
Mithril Capital focuses on funding companies that are beyond the startup stage but still have significant growth potential.
Co-founded Valar Ventures, a VC firm focused on global fintech startups.
Valar Ventures primarily invests in international financial technology startups, especially in Europe and Latin America.
Left Facebook’s board in 2022, after being a director for nearly two decades.
His departure was seen as a political move, as he wanted to focus more on influencing conservative politics in the U.S.
Wealth & Influence
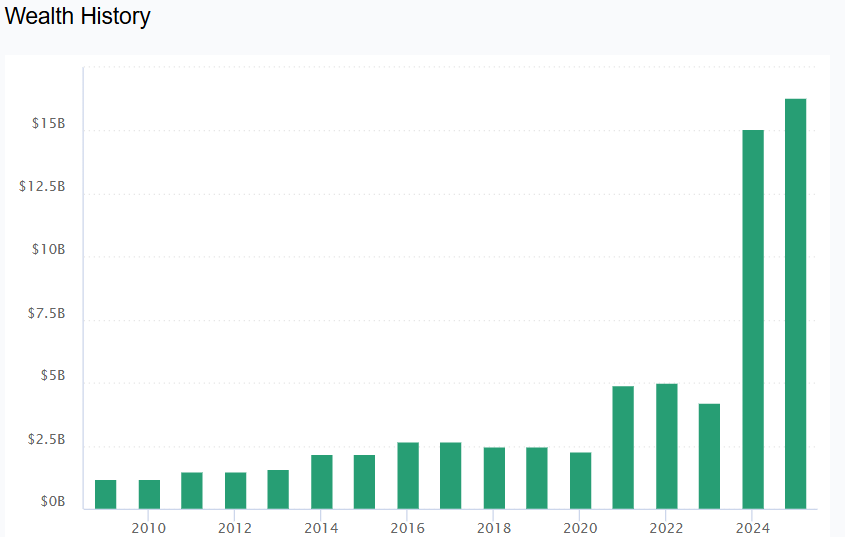
As of 2024, his net worth is estimated to be around $9 billion.
His fortune comes primarily from PayPal, Facebook, Palantir, and his venture capital investments.
Was ranked #4 on the Forbes Midas List in 2014 for top tech investors.
The Midas List ranks venture capitalists based on their deal success. Thiel was recognized for his early Facebook investment and other tech bets.
Known for supporting seasteading, an idea for independent floating city-states.
Thiel has funded The Seasteading Institute, which explores building autonomous communities in international waters to escape government regulation.
Supports longevity research, funding companies like Unity Biotechnology and investing in anti-aging initiatives.
He has repeatedly stated that he wants to live much longer than the average human lifespan and funds research into reversing aging.
Funded the Thiel Fellowship, which pays young entrepreneurs $100,000 to drop out of college and build startups.
This fellowship reflects his skepticism about traditional education and encourages young innovators to pursue business ideas instead.
Politics & Controversy
A strong libertarian, he has criticized high government regulation and centralization.
Thiel believes that excessive government intervention stifles innovation and economic freedom.
Was a major supporter of Donald Trump in the 2016 U.S. presidential election.
He was one of the few Silicon Valley figures to openly back Trump, donating $1.25 million to his campaign.
Secretly funded Hulk Hogan’s lawsuit against Gawker, which led to the media company’s bankruptcy.
After Gawker outed him as gay, Thiel funded Hulk Hogan’s privacy lawsuit against the website, ultimately leading to its downfall.
Criticized Silicon Valley’s left-leaning politics, calling it an ideological “one-party state.”
He argues that Silicon Valley suppresses conservative viewpoints and lacks political diversity.
Has expressed skepticism about higher education, calling it an expensive and ineffective system.
Thiel believes that many degrees do not provide a good return on investment and that entrepreneurship is often a better path.
Peter Thiel, a billionaire entrepreneur and investor known for his contrarian views and significant influence in Silicon Valley and beyond. Key themes emerging include:
Thiel's Philosophy and Worldview: He is described as an anti-democratic figure espousing a "dark enlightenment" philosophy, a technocratic, neo-feudalistic worldview that questions the compatibility of democracy and freedom. He's also associated with libertarianism and a critique of modern society.
Contrarianism and Definite Thinking: Thiel is characterized by his contrarianism and advocacy for "definite thinking." This involves having a concrete vision for the future and actively working to shape it, as opposed to "indefinite thinking" which is marked by uncertainty and reliance on incrementalism.
Critique of Higher Education and Stagnation: Thiel is critical of higher education, seeing it as a corrupt system that distracts from real progress. He argues there is a general stagnation in science and technology outside of the computer context.
Mimetic Desire and Scapegoating: Thiel is deeply influenced by the theories of René Girard, particularly mimetic desire (that human desire is copied) and the role of scapegoating in society.
Investment and Business Ventures: Thiel has been involved in several successful companies, including PayPal, Palantir Technologies, and Founders Fund, reflecting his ability to identify and capitalize on opportunities.
Political Influence and Controversies: Thiel's political views and financial support of conservative figures, including Donald Trump and J.D. Vance, have made him a controversial figure. He has been accused of anti-democratic tendencies and promoting divisive ideologies.
Obsession with Mortality and Anti-Aging: A recurring theme is Thiel's fascination with death and his investment in anti-aging technologies.
Detailed Themes and Ideas:
The "Dark Enlightenment" and Anti-Democratic Tendencies:
The Barrett Brown source characterizes Thiel's philosophy as a "technocratic like Neo feudalistic obscurist fastest you know ethos."
Thiel questions the compatibility of democracy and freedom: "I don't think democracy and freedom are compatible anymore."
Concerns are raised about Thiel's past actions, including targeting dissident journalists and labor union leaders, suggesting a willingness to undermine democratic processes.
Alexander Karp of Palantir is mentioned as not sharing the same philosophy as Thiel, suggesting internal conflicts of ethics within the company.
Definite vs. Indefinite Thinking:
According to the "Definite vs. indefinite thinking: Notes from Zero to One by Peter Thiel – Box Kite Machine" source, Thiel believes one can choose to think of the future in definite or indefinite terms.
Definite thinking favors "firm convictions" while indefinite thinking is where "people lack concrete plans to carry out, they use formal rules to assemble a portfolio of various options."
Definite optimists "led the Western world" from the 17th century through the 1960s with examples such as the Golden Gate Bridge, The Manhattan Project, and the Interstate Highway System.
Thiel criticizes the "lean startup" methodology as leading to "local maximum," not "global maximum."
Critique of Higher Education and Scientific Stagnation:
Thiel believes that Academia is something that he has "never forgiven" and he's very angry about.
The "Peter Thiel: "Diversity Myth" 30 Years Later" document states that Thiel believes there has been general stagnation in science and technology outside of the computer context.
He suggests "all the craziness in the humanities served the administrators well because it stopped people from asking questions about the crown jewels which were the sciences."
Thiel argues universities don't prepare students to enter society or perform.
Mimetic Desire and Scapegoating (Girardian Influence):
The Ethical Systems source highlights Thiel's interest in René Girard's mimetic theory, "that humans unconsciously imitate the desires of others."
Business Acumen and Investments:
The "Chess Concepts Peter Thiel Used To Become A Billionaire | Psychology Today" source, suggests the game of chess is in some ways reflected in the way he strategizes.
The "Peter Thiel: Peter Thiel Net Worth, Biography, Age, Spouse, Children & More - Goodreturns" source says that Thiel co-founded PayPal and Palantir Technologies, among other companies.
Early investment in Facebook showed his ability to identify lucrative opportunities.
Political Controversies and Influence:
The "Part One: How Peter Thiel Became the Gravedigger of Democracy | BEHIND THE BASTARDS" source portrays Thiel as potentially "methodically destroying" representative democracy, but whether that is the intent or an indirect consequence, is not known.
Thiel backed Trump early in 2016, which is described as supporting "the Republicans to the hilt in order to hopefully crumble the system of democracy enough that like he gets to rule his own little bitty city somewhere on the west coast."
According to one source, Thiel defended apartheid, stating it "was a sound economic system working efficiently and moral issues were irrelevant." Thiel has denied this, but a classmate recalls the exchange differently.
The Stanford Review, a magazine he founded, featured controversial content on homosexuality and the AIDS epidemic.
Obsession with Mortality and Anti-Aging:
The "Part One: How Peter Thiel Became the Gravedigger of Democracy | BEHIND THE BASTARDS" source explains that Peter's dad explaining death to him while looking at a cowhide rug, stuck with him throughout his life.
He invests in companies that research anti-aging.
"Diversity Myth" and Culture Wars:
Thiel co-authored "The Diversity Myth," which critiqued multiculturalism on college campuses. He now believes the arguments in the book were specifically correct, but missed the bigger picture.
According to the Thiel on secrets and indefiniteness — Thiel's excerpts say there are "no blank spaces left on the map anymore," referring to geographical discoveries.
Contradictions and Nuances:
The "Part One: How Peter Thiel Became the Gravedigger of Democracy | BEHIND THE BASTARDS" source is split on whether Thiel is a "master plotter" or a man who is intelligent and has okay instincts.
While some sources portray him as a cold and calculating figure, others suggest a more complex personality, marked by loneliness and a desire to escape reality.
Conclusion:
Peter Thiel is a highly influential figure whose worldview challenges conventional thinking. His contrarian nature, combined with his financial power and willingness to support unconventional ideas, has made him a significant force in business, technology, and politics. Understanding his core beliefs and motivations is crucial to understanding his impact on society.
Sources:
https://www.thielfoundation.org/
https://foundersfund.com/
https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20240320742346/en/Thiel-Foundation-Announces-Next-Thiel-Fellow-Class
https://perell.com/essay/peter-thiel/
https://perell.com/essay/peter-thiel-interview/
https://www.educationnext.in/posts/why-peter-thiel-does-not-believe-in-the-higher-education
https://www.playforthoughts.com/blog/peter-thiels-principles
https://www.businessinsider.com/peter-thiel-childhood-11-surprising-details-the-contrarian-max-chafkin-2021-9
https://foundersfund.com/our_team/
https://www.reuters.com/technology/peter-thiels-founders-fund-made-200-million-crypto-investment-before-bull-run-2024-02-13/
https://fortune.com/2024/12/07/peter-thiel-network-trump-white-house-elon-musk-david-sacks/













Share this post